PETG filament
(Polyethylene terephthalate glycol)
Basic Info
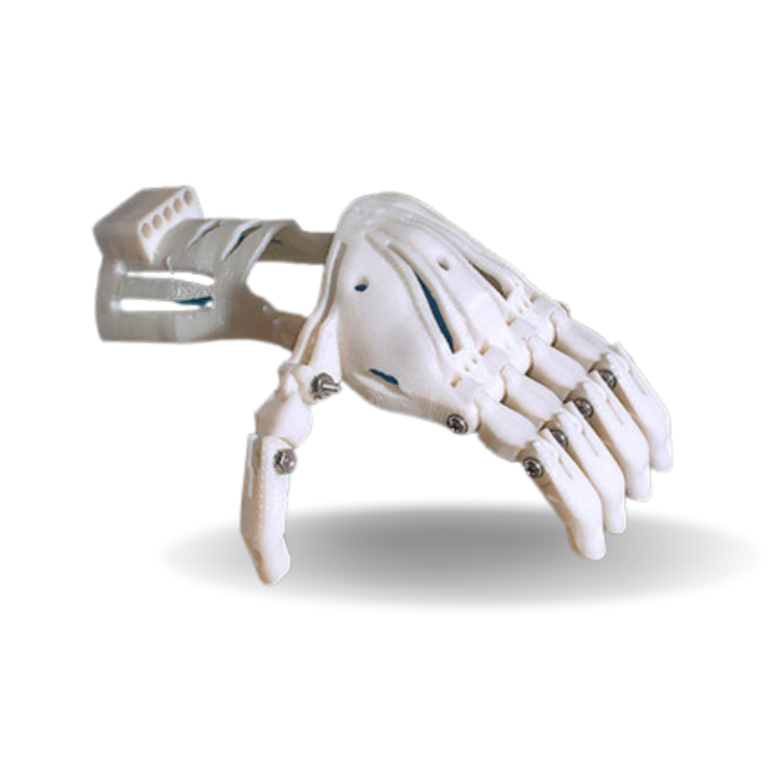
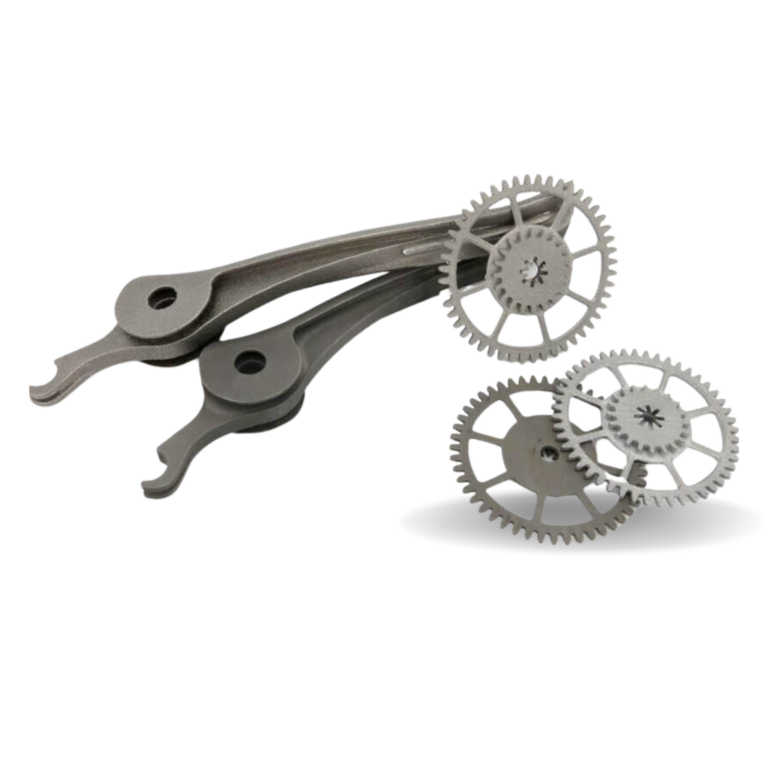
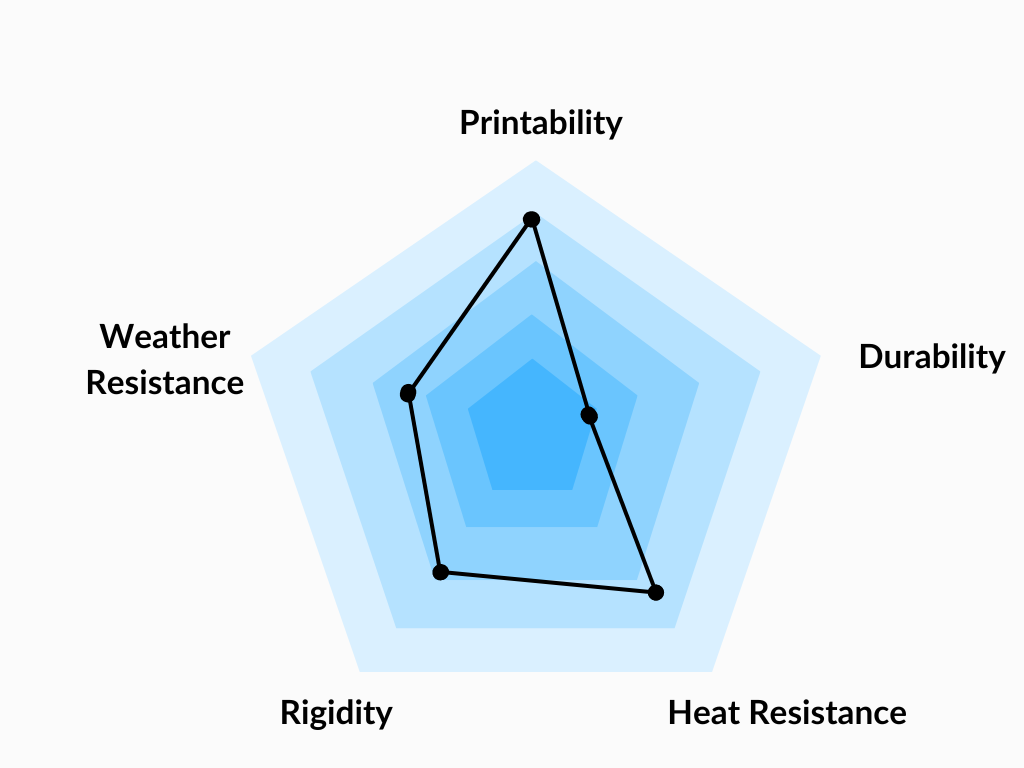
PETG Filament is one of the most easily printable materials, it is inexpensive and suitable for beginners. Relatively high tenacity and temperature resistance make it suitable for printing technical parts (for example parts of our printers).
Description
PETG filament (Polyethylene Terephthalate modified with Glycol) is a commonly used technical material, popular among 3D printer users for its low price and good printability. It’s tenacious, with good temperature resistance; PETG is most commonly used for printing various mechanical parts, holders, clamps, and waterproof parts (thanks to great layer adhesion).
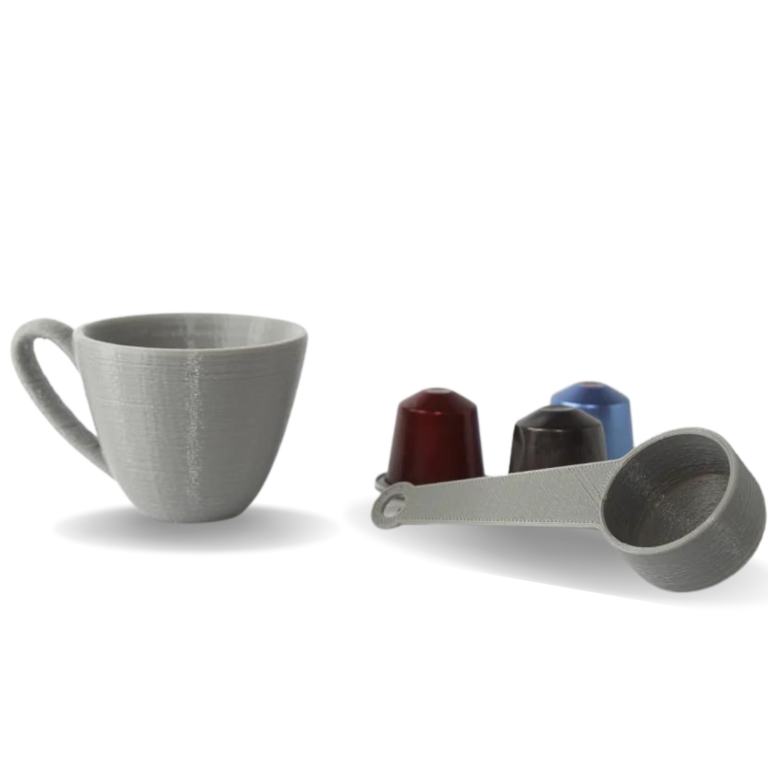
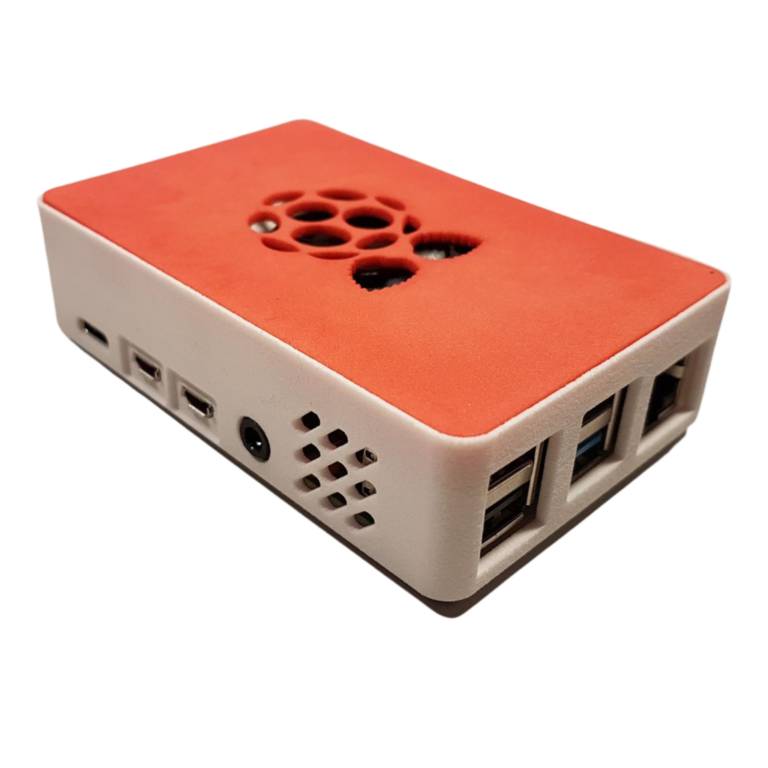
PETG filament has a glossy surface, adheres greatly to a print sheet, and does not shrink or warp (it has very little thermal expansion), therefore it’s suitable for printing large models. Plus, its high tenacity and flexibility often prevent it from breaking. Due to good temperature resistance, PETG parts are suitable both for interior and most exterior use (with temperatures below 80 °C). Parts of our printers are made of PETG!
The letter G in PETG means that it’s modified with glycol during the manufacturing process. Glycol makes PET less brittle, easier to print, and more transparent for translucent prints. Of course, you can print also with PET filaments without glycol. However, printing with only PET is challenging and does not offer any advantage whatsoever.
Chart
Pros and Cons of using PETG filament
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Strong and impact resistant like ABS and warps less | Prone to stringing |
| Excellent layer adhesion | bad as support material or for bridging |
| Nice surface finish with glossy translucent look | Scratch resistance |
Applications
Food and Drink Containers
Because it has good chemical resistance and is easy to thermoform, PETG is widely used for items such as cooking oil containers, drinking bottles and FDA-compliant food storage containers. It is also used for cosmetics packaging and the light weight and high strength delivers advantages for distribution costs and effectiveness.
Medical and Pharmaceutical Applications
The rigid structure of PETG means that it can survive harsh sterilisation processes, which makes it an ideal substance for medical implants as well as packaging for pharmaceutical and medical devices.
Retail Stands and Displays
polyethylene terephthalate glycol is widely used for point-of-sale retail stands and displays. Since it can be colored, it is also ideal for signage.
Machine Guards
PETG filament is also used to manufacture machine guards. The clear plastic is easy to form while also offering protection for users. PETG guards are often used in food processing as they are easier to form than polycarbonate and more durable than acrylic.
3D Printing
As mentioned above, PETG filament has gained popularity for use in modern 3D printers. A polyethylene terephthalate glycol filament prints easily and provides excellent layer adhesion. Low shrinkage rates allow for larger prints than with PLA or ABS, while PETG is also strong, chemical resistant and odorless while printing. It is advised that a cooling fan is used while printing with PETG, while problems with printing bed adhesion can be overcome by putting down a layer on the build plate.